Human papillomavirus (HPV) affects epithelial cells and has a particle diameter of 55 nm. A special feature is the proliferation of the epithelium of the skin, as well as the mucous membrane. In the initial stage, the pathogen usually affects the basal cells of the epithelium, penetrating them through microtraumas. Localized papillomas are most often found on the skin of the neck, armpits, groin and genitals (mostly), oral mucosa and nasopharynx.
This virus can live without symptoms for many years. To detect HPV, electron microscopy or molecular hybridization methods are used.
Types of human papillomavirus
Humans have HPV that affects the mucous membranes and skin. Among the many papillomaviruses, there are low and high oncogenic risk types. Oncogenic properties have been shown to be related to the ability of human cells to integrate DNA into their genome.
The virus is activated in 10-20% of cases. Depending on its type, it can cause benign or malignant lesions. Some HPVs are not oncogenic. They cause warts and genital warts. The most common are HPV 6 and 11.
HPV oncogenes are the ones that increase the risk of developing cancer, especially in the cervix or anus. As for the skin, HPV 16 and 18, as well as 5 and 8, which cause skin cancer, are more common. The most common type of cancer caused by HPV is cervical cancer. But men can also be infected with the papilloma virus, which in the worst cases can cause cancer of the penis or anus.
Most often, women are found with HPV 16 - this is the form in which intrasomal parasitism is observed, p. a. outside the cell chromosome (good). HPV 18 carries a high risk of cancer - first benign tumors appear, which after some time turn into cancer. In this case, virions have small sizes (up to 30 nm).
- tumors of the cervix;
- invasive or pre-invasive oncology;
- Urinary and genital warts.
Features of infection

Human papillomavirus is highly contagious. It is usually spread by direct contact with an infected person, skin-to-skin or mucous membrane-to-mucous membrane. For genital infections, this usually occurs during vaginal or oral sex. Having multiple sexual partners or other STDs (sexually transmitted infections) increases the risk. It can be transmitted indirectly through objects, contaminated clothing or bedding, but is very rare.
In 7% of cases, mother-to-child transmission of the virus may occur during childbirth, when the infection is active. If infected with HPV 16 or 18, the risk increases to 40%.

Penetrating the epithelium and destroying its integrity, the papillomavirus infection contributes to the growth of the lower layer of epithelial cells in the form of condylomas or warts. This type of disease is contagious and spreads quickly to others. As a rule, warts and condylomas do not metastasize and often disappear on their own.
HPV symptoms
The incubation period lasts up to 9 months (average 3 months). HPV can be present in the body without obvious symptoms. The virus can go undetected for months or years. This stage is also contagious.
Skin warts usually appear in clusters and multiply when scratched. The two most common types of papillomas are grayish, hard, with a broken surface (common wart) or flat and pink (flat wart). Spiny warts appear on the soles of the feet or heels, grow inward, and are therefore often painful.
- Genital warts. Gray or reddish nodules that usually appear in clusters and appear on the labia, vulva, urethra, anal canal, and rectal surface. They are highly contagious.
- Flat condylomas. They appear in the form of flat nodules and are found mainly in the genital organs of women. They increase the risk of cancer.
- Giant condylomas (Buschke-Levenstein tumors). They destroy the surrounding tissue and become large structures. In rare cases, they can worsen and lead to squamous cell carcinoma.
An upper respiratory tract infection may also occur. The conjunctiva of the eye is affected, resulting in the appearance of a pink stalk.
Asymptomatic course is more difficult to detect, it can be seen by the doctor only with the help of aids such as acetic acid (which causes warts to change color) or microscope.
In addition, the virus can survive in cells without any tissue changes. Then they talk about latent infection, that is, the presence of pathogens, but no symptoms. After infection, this phase can last from several weeks to several months.
Possible consequences
When infected, viruses enter the cells of the skin and mucous membranes, settle in the nuclei of cellular structures, and multiply there. As a rule, this type of HPV infection is invisible and ineffectively heals on its own, because the immune system successfully fights the pathogen.
However, some types of HPV cause skin changes called growths. Possible forms include genital warts or condylomas and papillomas, which can affect the face, hands or feet, for example.
The resulting tissue changes are mostly benign, but they can also be damaged and cause cancer. For example, cancer can develop decades after HPV infection. Cancer of the female external genitalia (cancer of the vulva and vagina), anal cancer, cancer of the penis, and cancer of the mouth and throat (tumors of the head and neck) are also possible.
Make a diagnosis

As part of a preventive visit to a gynecologist, women are tested for HPV infection. During a gynecological examination, a smear is taken from the mucous membrane of the cervix, which is called a Papanicolaou test (cytological examination). The removed material is examined for tissue changes to detect precancerous conditions.
In addition, an HPV test may be performed, in which cellular material taken from a mucosal swab or tissue sample is tested in a laboratory for the presence of certain viruses. However, this only proves that the affected area is infected, but does not make any statements whether tissue changes have occurred or not. Thus, the HPV test makes sense, especially when combined with a Pap test, and helps detect cancer precursors at an early stage.
If the test is positive, there is no need to worry because infections do not always lead to cancer. Regular examination is recommended to detect tissue changes at an early stage. Conversely, a negative test result does not indicate the presence or absence of a past infection that the body successfully fought off.
There is no routine screening for men. If an underlying cancer is present, analysis of the tumor can determine whether HPV infection is underlying the cancer.
Specialized DNA techniques are also used in laboratory diagnostics such as real-time PCR. Anogenital warts caused by HPV types 6 and 11 are easily detected during a gynecological examination.
How to cure human papillomavirus

In most cases, the disease goes away on its own, and after that the viruses are not detected, so it does not require treatment. However, if not, the infection may persist for months or years.
To date, there are no methods of systemic exposure to this virus that can completely eliminate it. However, treating existing warts reduces the number of viruses, so in many cases the immune system can fight off the remaining viruses and get rid of them. In some cases, pathogens can survive and repeatedly cause symptoms of the disease.
- Varicose veins and genital warts can be treated with salicylic acid topical medications.
- Cryotherapy is also a commonly used treatment for HPV. In this case, the wart is burned with cold using liquid nitrogen.
- Laser or electrocautery is used equally.
Cancer caused by HPV is much more difficult to treat. For cervical cancer, it is often recommended to remove the uterus, the vagina, and the upper part of the ovary, respectively. This may be supplemented with radiation therapy to eliminate the possibility of recurrence. Other cancers caused by HPV are often treated with targeted therapies such as radiation or chemotherapy.
It should be remembered that this operation is not a radical solution, but only solves a cosmetic problem, because after removal, the virus can remain in the surrounding tissues and condylomas can reappear.
Prevention of infection
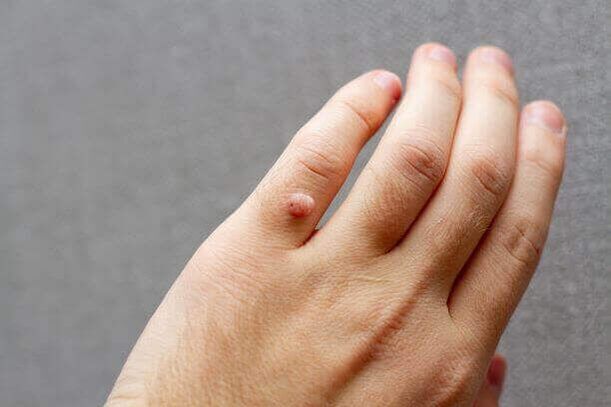
There are two vaccines: the bivalent vaccine against HPV 16 and 18 and the quadrivalent vaccine against HPV 6, 11, 16 and 18. Vaccination is recommended for all young women over 14 years of age.
Vaccination does not protect against all types of HPV. Therefore, all women between the ages of 25 and 65 are recommended to have regular Pap smears, even if they have been vaccinated.
Timely detection and complete removal of condyloma reduces the risk of developing the disease. The effectiveness of condom use to prevent transmission of infection significantly reduces the risk of developing this disease. The most promising way to prevent and treat the early stages of the disease caused by this infection is a specific polyvalent vaccine.
Why plantar warts occur and treatment methods
Warts are skin lesions that appear in the form of special round formations that protrude above the surface. They are caused by certain viruses.
These structures often cause physical discomfort due to their location. Even after treatment, they recur.
Types and causes
There are many types of warts, which are divided according to a number of characteristics:
- Easy going. They appear on exposed parts of the body, hands, feet, face and scalp. They are usually not dangerous, but they are not aesthetically pleasing and affect large areas of the skin, multiplying quickly. They are arranged as in "families".
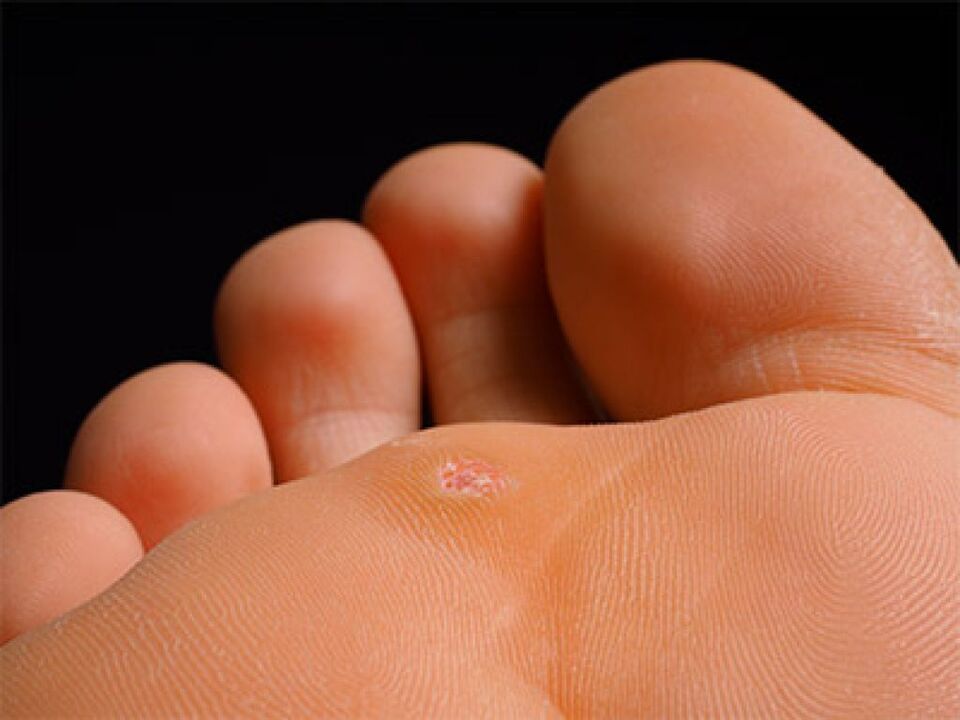
- Plantar. Their localization is only on the feet. It causes discomfort when walking.
The main cause is human papillomavirus infection, which affects the mucous membrane and skin.
Human papillomavirus
It is one of the most common viruses on earth. Infection can occur in several ways:
- communication and life (through touch);
- sexual (sex, anal, oral-sex);
- from mother to child in childbirth.
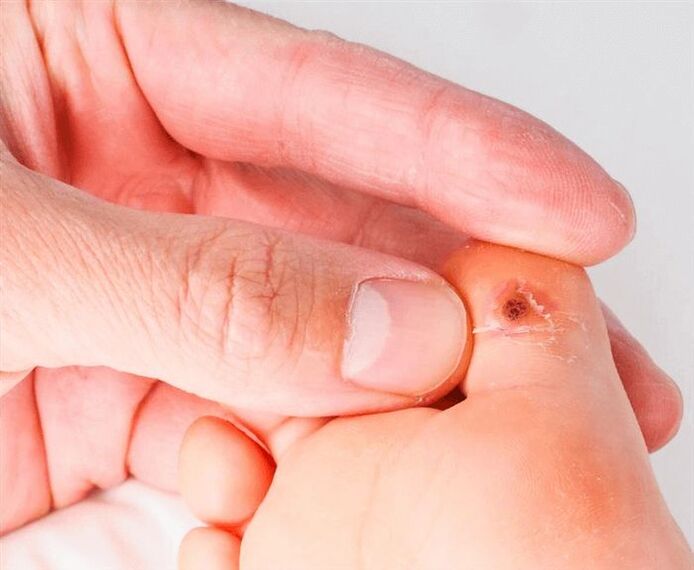
The period of development of the disease lasts from several weeks to decades, which is explained by the fact that the virus does not show itself for a long time, but when the immunity begins to weaken a little, immediate growths appear. skin and/or mucous membranes. The main danger of this disease is that some types of HPV can cause the formation of malignant tumors (cancer of the skin or mucous membrane). To make sure that the pain does not lead to the formation of tumors, it is necessary to undergo a doctor's examination and self-medicate.
Signs and types of warts on the feet
Plantar warts appear as callus-like thickening of the horny layer of the skin. It prevents walking and causes pain. The passive state is characterized by a slow proliferation that does not reach the stratum corneum of the epithelium, so this state is not visible from the outside.
The active state is characterized by the rapid development of the virus and its rise to the upper layers of the epidermis, with many symptoms. Plantar warts are also called chicken warts. When the virus comes into contact with the skin, it enters through cuts and abrasions in the outer layer of the skin:
- First, a small yellowish-gray papule with an uneven surface appears.
- Gradually, the small element becomes dense and acquires a dirty color.
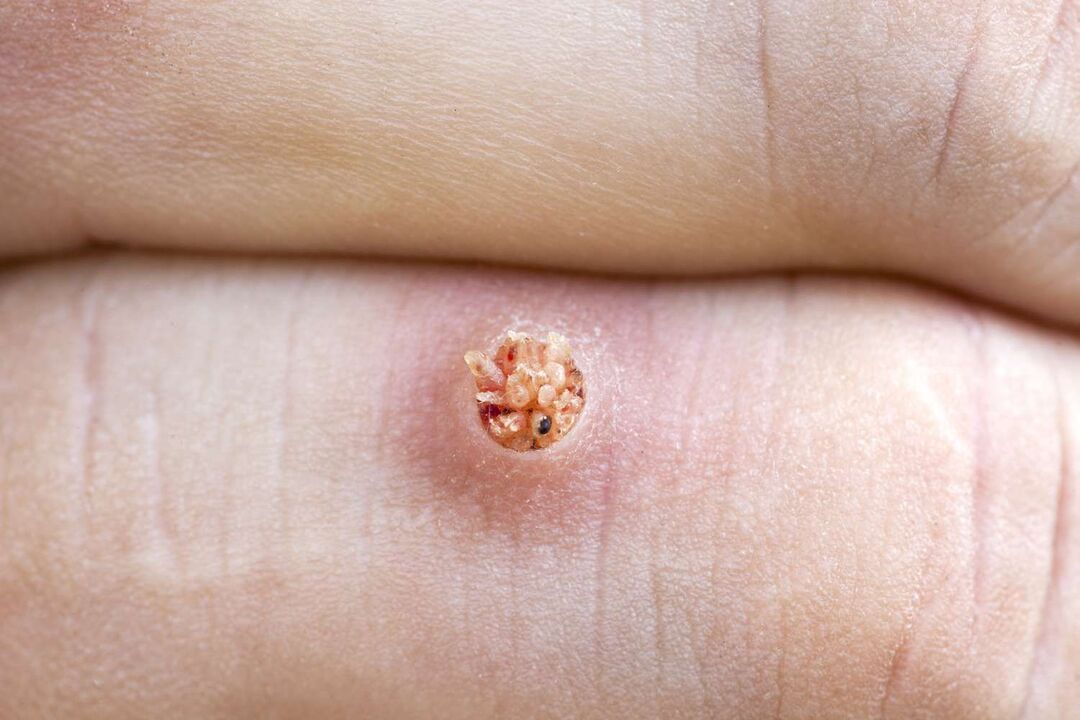
From the inside, plantar warts look like swollen papillae of various sizes, pink in color. Extra capillaries form there, and if you touch the wart, it will cause bleeding.
Removal of plantar warts
Plantar warts should be treated if:
- There are painful feelings.
- The wart is bleeding.
- It had spots on it.
- Warts grow quickly.
There are many treatment options. One of them is cryodestruction. The meaning of the method is that the wart is exposed to liquid nitrogen at a temperature of minus 196 degrees. The infected area is frozen and the wart is removed.
A conventional and aggressive exposure method is used. With the more aggressive method, nitrogen is used for a few more seconds, but this method is more painful. It should be noted that if warts appear and exist for more than six months, the effectiveness of cryodestruction is greatly reduced and the value of such an operation is lost.
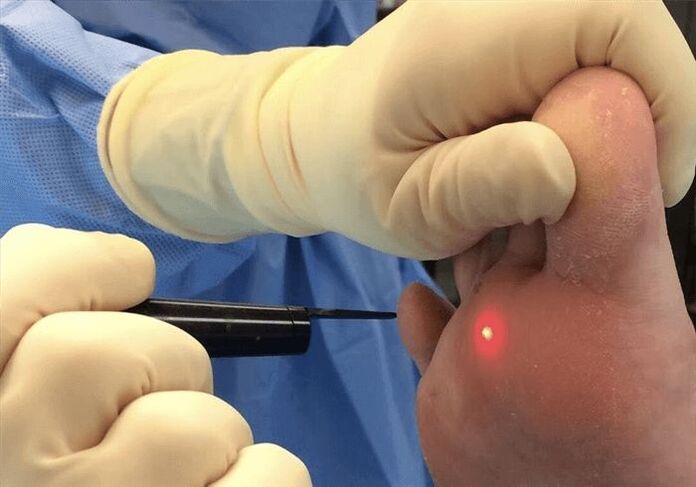
After removing a plantar wart with liquid nitrogen, you should follow some recommendations:
- it is impossible to open the blister left in place of the wart;
- use a sterile bandage, not a plaster, to avoid mechanical damage;
- Treat the affected area with salicylic alcohol 2% twice a day;
- Try to keep water out of the affected area.
Another method is laser coagulation. This is one of the most common ways to get rid of warts. Most laser systems are equipped with a special cooling system. Thus, the procedure takes place with minimal discomfort and prevents inflammation, because the laser has antiseptic properties. Moreover, it is a non-contact method.
There are several ways:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) laser. In this case, the treatment is carried out with the help of infrared light. The method is 70% effective, but the downside is that healthy tissue is damaged.
- Erbium laser. This treatment method uses short wavelengths to reduce the likelihood of scarring after surgery. Efficiency is usually 75%.
- Pulsed dye laser. With this method of exposure, the first destruction of the dilated capillaries in the wart and the stimulation of the immune system contribute to effective healing. The effectiveness of treatment is about 95%.
After laser treatment, a crust will form on the affected area, which will disappear on its own within seven to ten days. Recommendations for this method of treatment are the same as for exposure to nitrogen - avoid mechanical damage and water ingress.
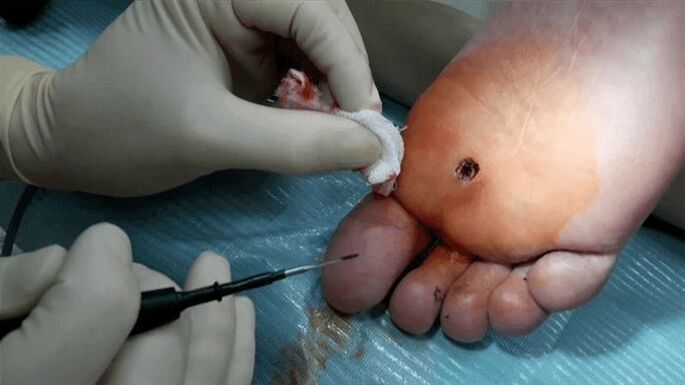
The next way to remove warts is electrocoagulation. In this case, a high-frequency current is applied to the wart. Treatment is performed under local anesthesia. The effect of high temperature on the wart leads to evaporation of the cells affected by the papilloma virus. Another advantage of this method is that cauterization of blood vessels prevents bleeding. After the operation, a crust will appear on the affected area of the skin, which will disappear within 7-10 days.
Plantar warts can be treated with direct surgery. In this case, the incision is made under local anesthesia, and then sutures are applied. After the operation, the doctor will prescribe certain recommendations. Thus, it is recommended not to allow water and soap to enter the affected area, not to break the formed crust and to treat the affected area with an antiseptic in the first 7-10 days.
There are certain contraindications for each type of operation. Thus, the operation cannot be performed when the following occurs:
- pregnancy;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- malignant tumors in the body;
- infection and inflammation around the wart;
- exacerbation of herpes;
- elevated temperature.
If you have high blood pressure, the procedure should also be postponed.
Treatment of warts without surgery

People often wonder how to get rid of plantar warts without surgery. For this, you can use pharmaceutical oils and solutions.
Basically, these oils have the following effects:
- anti-inflammatory;
- antiseptic;
- immunomodulatory;
- anti-virus;
- anti-fungal.
In addition, it may contain vitamin E, which also has a positive effect on treatment, as vitamins generally strengthen the body and reduce the risk of relapse.
These products should be used for single and shallow warts. In addition, if any side effects occur, wash the medicine with warm water and consult a doctor immediately.
So warts can be cured, there are many ways to do it, but don't do it without consulting a doctor first to avoid harming your health. In addition, it is strictly forbidden to self-medicate, if the attending physician has contraindications.
Treatment of papillomas on the body
Hardware methods
Modern hardware methods of treatment of papillomas allow to get rid of them and prevent recurrence of the disease. The most commonly used methods are:
- Cryodestruction is the destruction of growths under the influence of low temperature.
- Electrocoagulation is cauterization of structures with electric current, its power and frequency are selected depending on the size, type and density of the papilloma.
- Laser removal. The type of effect is obvious from the name. The procedure takes no more than 15 minutes and helps to get rid of unwanted growths forever.
Drug treatment
Among the drugs used are chistotela, castor oil, lapis pencil, Sani Skin and Dermavit preparations.
They show different effectiveness and do not prevent recurrence of the disease. The main disadvantage of drug therapy for papilloma is the frequent development of allergic reactions.
Prevention of papillomas
To prevent growths and human papillomavirus infection, it is necessary to:
- Use a barrier barrier during intercourse.
- Follow the rules of personal hygiene and use only personal towels, soap and toothbrush.
- Remember to wear rubber shoes when visiting public baths.
It is also necessary to normalize the daily routine, eat a balanced diet, avoid bad habits and avoid stressful situations. These factors are not the cause of the disease, but if there is a virus in the body, they can stimulate its development.














































































